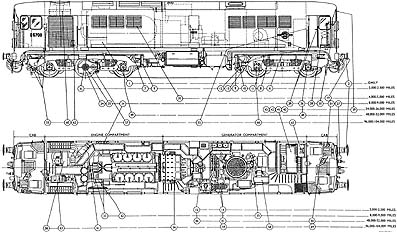
Fig. 13. Lubrication Diagram
If the locomotive is inspected regularly and methodically, the cost of repairs will be kept low, and the life of the equipment lengthened. The procedure recommended in this section should, however, be used as a guide, until operating experience shows what intervals may be used safely. For example, the lubrication of the bearings of electrical machines depends on the needs of the service, and should be determined from controlled observations on several locomotives.
It is assumed that, on average, the locomotive will cover about 300 miles per day, and that the diesel engines will run for about 100 hours per week.
For engine air fitter panels and fuel pump parts, etc., it will be more satisfactory to exchange them for ready-cleaned or reconditioned parts.
For the boiler, the schedule is drawn up on the assumption that the boiler is in full-time operation.

Fig. 13. Lubrication Diagram
| Daily Check the fuel, water and lubricating oil supplies. Check that there are no leakages of fuel, lubricating oil, servo oil, or water, and that the drain cocks are securely closed. Engine Check that all cylinders are cut in, with their lever points down, and that the overspeed trip is latched in the correct position. Control Equipment Brake and Air Equipnient Mechanical Parts Boiler Lubrication |
| Weekly = 2000 to 2500 miles = 100 hours Daily routines plus :- Engine Control Equipment Brake and Air Equipment Mechanical Parts Boiler Lubrication |
| Monthly = 8000 to 9000 miles = 500 hours Weekly routines plus :- Engine Control Equipment Electrical Machines Brake and Air Equipment
(2) Snifter valve - Dismantle, clean and test after reassembly Mechanical Parts Boiler The instructions for items 6 and 7 are provisional until the correct water treatment has been determined. Lubrication |
| Three-monthly = 24000 to 26000 miles = 1250 hours Monthly routines plus :- Engine Control Equipment Electrical Machines Brake and Air Equipment Mechanical Parts Boiler Lubrication |
| Six-monthly = 48000 to 52000 miles = 2500 hours Three monthly routines plus :- Engine Control Equipment Brake Auxilliary Equipment Mechanical Parts Boiler Lubrication |
| Annually = 96,000 to 104,000 miles = 5000 hours Six monthly routines plus :- Engine Control Equipment Brake and Air Equipment Few replacements are to be expected after one period, and after two periods replacements will probably be confined to 'O' Rings, seals and gaskets Mechanical Parts Boiler Lubrication |
| General overhaul (At approxi. 3-year intervals.)
Engine Control Equipment (1) All insulation - Clean, and repair any damage Electrical Machines Examine all parts thoroughly, and clean, renovate or renew as required. When they are reassembled, the machines should be run light long enough to ensure that the bearings fit correctly. If necessary, the machines should be dried out, and possibly revarnished and again dried out, before going back into service. Mechanical parts Boiler |
LUBRICATION-TOPPING-UP LEVELS
The correct levels are:-
Diesel Engine Sump
Between the FULL and REFILL marks on the dipstick (the dipstick is not screwed down), after priming and with the engine stationary.
Exhauster Sump
Between the top and bottom of the strainer in the oil filler, with the exhauster stopped.
Compressor and Dynamic Balancer Sumps
Between the high and the low marks on the compressor dipstick, with oil to the level of the level plug in the balance weight chamber. When filling the compressor, allow enough time for the oil to pass into the balance weight chamber before checking the levels.
Axle-boxes
When the levet plug is removed, it should be possible to see the oil rising up the plug hole.
Traction Motor Suspension Bearings
Between the MINIMIUM mark on the dipstick and the bottom of the filler pipe.
Traction Motor Gears
Between the MAXIMUM and MINIMUM marks on the dipstick.
Load-regulator
Between 3in. and 8in. from the top of the servo oil tank tank.
Boiler Feed Pump
Between the top and bottom of the dipstick.
Locomotive Data & Performance
Description
Driver's Controls, Instruments and Gauges
Driving Instructions
Special Instructions
Boiler Operation
General Maintenance & Lubrication Schedules